The aim of the Aga Khan Museum will be to offer unique insights and new perspectives into Islamic civilizations and the cultural threads that weave through history binding us all together. The hope is that the Museum will also be a centre of education and of learning, and that it will act as a catalyst for mutual understanding and tolerance.
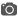
In designing the Aga Khan Museum, Fumihiko Maki, winner of the Pritzker Architecture Prize, used light as his inspiration. He ensured not only that light is ever-present in the building, but that, depending on the time of day or season, light will animate the building in myriad ways: throwing patterns on the exterior walls of Brazilian granite, enhancing interior spaces, or illuminating the open-roofed courtyard. The building’s compact footprint — 81 metres long and 54 metres wide — contains an impressive variety of spaces, including two exhibition galleries, areas for art conservation and storage, a 350-seat theatre, and two classrooms. Within an unmistakably contemporary design, Maki incorporates historical elements originating in Islamic cultures, building bridges between eras as well as civilizations.
Across from the Museum is the Ismaili Centre Toronto, designed by renowned architect Charles Correa. The Centre incorporates spaces for social and cultural gatherings, intellectual engagement and for spiritual reflection. Its crystalline frosted glass dome roof, which marks the highest point of the 6.8-hectare site, is mirrored in the five granite-lined pools of the formal gardens — designed by landscape architect Vladimir Djurovic — which are part of a landscaped park. The Aga Khan Park connects the Centre with the Museum and provides a place equally suited to tranquil reflection and dynamic programming.
Photo: "Aga Khan Museum in Toronto- Exterior" by JohnOyston - Own work. Licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0 via Wikimedia Commons - https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Aga_Khan_Museum_in_Toronto-_Exterior.jpg#/media/File:Aga_Khan_Museum_in_Toronto-_Exterior.jpg